5 Things You Should Know About RF Transceiver
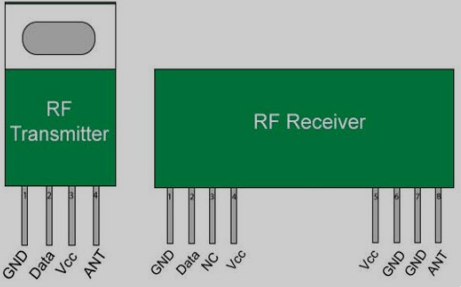
The other day, I was having a conversation with a friend about RF transceivers. He’s an electrical engineer and was asking me about my work as a digital marketing consultant. I explained to him that, although I don’t work specifically with RF transceivers, I do have a general understanding of the topic. After our conversation, it occurred to me that there are probably many people out there who are in the same boat as my friend. They may have a general understanding of RF transceivers, but they don’t really know what they are or how they work. If you’re one of those people, this blog post is for you.
Below, you’ll find five things you should know about RF transceivers.
1. RF transceivers are used in a variety of wireless applications.
2. They are typically used to transmit and receive radio signals.
3. RF transceivers come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
4. They can be used for both short-range and long-range communication.
5. RF transceivers typically operate in the frequency range of 30 MHz to 3 GHz.
What is an RF Transceiver?
An RF transceiver is a device that can send and receive radio signals. It is used in a variety of applications, including wireless communication, radar, and satellite systems.
RF transceivers are used in a wide range of applications, such as wireless communication, radar, and satellite systems. In a typical application, an RF transceiver can send and receive radio signals over the airwaves. The device usually consists of two parts: a transmitter and a receiver.
The transmitter converts electrical signals into radio waves, which are then sent out through an antenna. The receiver converts incoming radio waves into electrical signals that can be processed by electronic devices.
RF transceivers come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the specific application. For example, handheld radios typically use small and lightweight transceivers, while base station radios used in cellular networks tend to be larger and more powerful.
RF transceivers typically operate over a wide range of frequencies, from low-frequency (LF) to ultra-high-frequency (UHF). The frequency band that a particular transceiver can operate in is determined by its design. Transceivers that can operate in multiple frequency bands are known as multi-band or multi-mode TPS7B8250QDGNRQ1 transceivers.
How does an RF Transceiver Work?
An RF transceiver is a device that transmits and receives radio frequency signals. The two components of the RF transceiver are the transmitter and receiver.
The transmitter takes the input signal and encodes it onto an electromagnetic carrier wave. The encoded signal is then amplified and sent out through an antenna.
The receiver takes in the incoming signal from the antenna. The signal is then amplified and decoded to retrieve the original input signal.
What are the Benefits of an RF Transceiver?
Radio Frequency (RF) transceivers are becoming increasingly popular as they offer a number of advantages over traditional transceivers. Here are some of the benefits of using an RF transceiver:
1. Increased Range: RF transceivers can transmit and receive signals over much greater distances than traditional transceivers. This is due to the fact that RF waves can travel further and penetrate obstacles more easily than other types of waves.
2. Greater flexibility: RF transceivers offer greater flexibility in terms of frequency selection and modulation schemes. This means that they can be used for a wider range of applications than traditional transceivers.
3. Improved performance: RF transceivers typically offer improved performance in terms of sensitivity and selectivity. This means that they can provide clearer communication with less interference.
4. Lower cost: As technology has progressed, the cost of RF transceivers has fallen significantly, making them more affordable for many users.
What are the Different Types of RF Transceivers?
There are two main types of RF transceivers: surface-mount and through-hole. Surface-mount RF transceivers are smaller and easier to install, but through-hole RF transceivers are more reliable.
Surface-mount RF transceivers are typically used in consumer electronics because they are less expensive and easier to install. Through-hole RF transceivers are used in industrial and military applications because they can handle more power and are more reliable.
Which type of RF transceiver you need depends on your application. If you need a small, inexpensive transceiver for a consumer electronics application, a surface mount is probably the way to go. If you need a more powerful, reliable transceiver for an industrial or military application, a through-hole is the better choice.
How to Choose the Right RF Transceiver for Your Application
When it comes to RF transceivers, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. The right transceiver for your application will depend on a number of factors, including the frequency band you need to operate in, the data rate you need to support, the power consumption requirements of your system, and more.
In this first section of our blog series on things you should know about RF transceivers, we’ll take a look at how to choose the right RF transceiver for your specific application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an RF Transceiver
There are a number of factors that you need to consider when choosing an RF transceiver for your application. These include:
Frequency Band: One of the most important considerations when choosing an RF transceiver is the frequency band you need to operate in. Different transceivers support different frequency bands, so it’s important to make sure that you select a transceiver that operates in the same band as your system.
Data Rate: Another important consideration is the data rate you need to support. Different transceivers support different data rates, so it’s important to make sure that you select a transceiver with the right data rate for your application.
Power Consumption: Power consumption is another key consideration when selecting an RF transceiver. Some transceivers are more power efficient than others, so it’s important to select a transceiver that meets the power consumption requirements of your system.
Pros and Cons of RF Transceivers
RF transceivers have a number of advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before using them in any application. Some of the pros of RF transceivers include:
– They are very versatile and can be used for a variety of applications
– They offer high data rates and are relatively easy to use
– They are small and compact, making them easy to deploy
– They consume relatively low power, making them ideal for battery-powered devices
Some of the cons of RF transceivers include:
– They can be expensive compared to other types of transceivers
– They can be more complex to use than other types of transceivers
– They can be subject to interference from other devices
Conclusion
If you’re looking to add an RF transceiver to your project, there are a few things you should keep in mind. First, make sure that the transceiver you choose is compatible with the frequency you’re using. Second, consider the power output and range of the transceiver. Third, take into account the data rate and bandwidth that you need. Fourth, think about any special features that might be useful for your application. And finally, don’t forget to factor in the cost. By keeping these factors in mind, you can narrow down your choices and find the perfect RF transceiver for your project.


